10 KiB
Usage: build, setup and flight
To fly Flix quadcopter, you need to build the firmware, upload it to the ESP32 board, and set up the drone for flight.
To get the firmware sources, clone the repository using git:
git clone https://github.com/okalachev/flix.git && cd flix
Beginners can download the source code as a ZIP archive.
Building the firmware
You can build and upload the firmware using either Arduino IDE (easier for beginners) or command line.
Arduino IDE (Windows, Linux, macOS)
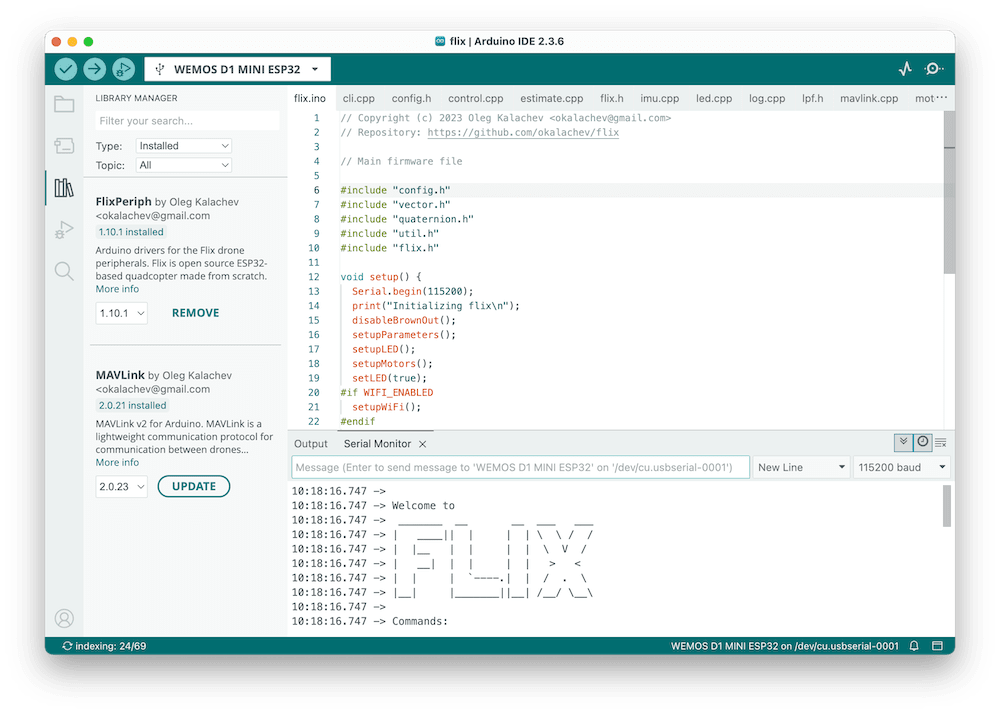
- Install Arduino IDE (version 2 is recommended).
- Windows users might need to install USB to UART bridge driver from Silicon Labs.
- Install ESP32 core, version 3.2.0. See the official Espressif's instructions on installing ESP32 Core in Arduino IDE.
- Install the following libraries using Library Manager:
FlixPeriph, the latest version.MAVLink, version 2.0.16.
- Open the
flix/flix.inosketch from downloaded firmware sources in Arduino IDE. - Connect your ESP32 board to the computer and choose correct board type in Arduino IDE (WEMOS D1 MINI ESP32 for ESP32 Mini) and the port.
- Build and upload the firmware using Arduino IDE.
Command line (Windows, Linux, macOS)
-
On Linux, install it like this:
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/arduino/arduino-cli/master/install.sh | BINDIR=~/.local/bin sh -
Windows users might need to install USB to UART bridge driver from Silicon Labs.
-
Compile the firmware using
make. Arduino dependencies will be installed automatically:makeYou can flash the firmware to the board using command:
make uploadYou can also compile the firmware, upload it and start serial port monitoring using command:
make upload monitor
See other available Make commands in Makefile.
Tip
You can test the firmware on a bare ESP32 board without connecting IMU and other peripherals. The Wi-Fi network
flixshould appear and all the basic functionality including console and QGroundControl connection should work.
Before first flight
Choose the IMU model
In case if using different IMU model than MPU9250, change imu variable declaration in the imu.ino:
ICM20948 imu(SPI); // For ICM-20948
MPU6050 imu(Wire); // For MPU-6050
Setup the IMU orientation
The IMU orientation is defined in rotateIMU function in the imu.ino file. Change it so it converts the IMU axes to the drone's axes correctly. Drone axes are X forward, Y left, Z up:

See various IMU boards axes orientations table to help you set up the correct orientation.
Connect using QGroundControl
QGroundControl is a ground control station software that can be used to monitor and control the drone.
- Install mobile or desktop version of QGroundControl.
- Power up the drone.
- Connect your computer or smartphone to the appeared
flixWi-Fi network (password:flixwifi). - Launch QGroundControl app. It should connect and begin showing the drone's telemetry automatically
Access console
The console is a command line interface (CLI) that allows to interact with the drone, change parameters, and perform various actions. There are two ways of accessing the console: using serial port or using QGroundControl (wirelessly).
To access the console using serial port:
- Connect the ESP32 board to the computer using USB cable.
- Open Serial Monitor in Arduino IDE (or use
make monitorin the command line). - In Arduino IDE, make sure the baudrate is set to 115200.
To access the console using QGroundControl:
- Connect to the drone using QGroundControl app.
- Go to the QGroundControl menu ⇒ Vehicle Setup ⇒ Analyze Tools ⇒ MAVLink Console.
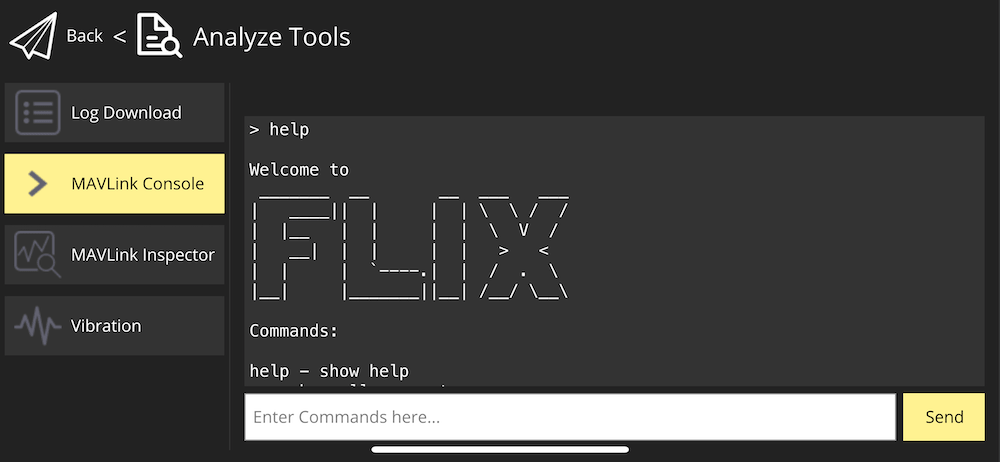
Tip
Use
helpcommand to see the list of available commands.
Calibrate accelerometer
Before flight you need to calibrate the accelerometer:
- Access the console using QGroundControl (recommended) or Serial Monitor.
- Type
cacommand there and follow the instructions.
Check everything works
-
Check the IMU is working: perform
imucommand and check its output:- The
statusfield should beOK. - The
ratefield should be about 1000 (Hz). - The
accelandgyrofields should change as you move the drone. - The
landedfield should be1when the drone is still on the ground and0when you lift it up.
- The
-
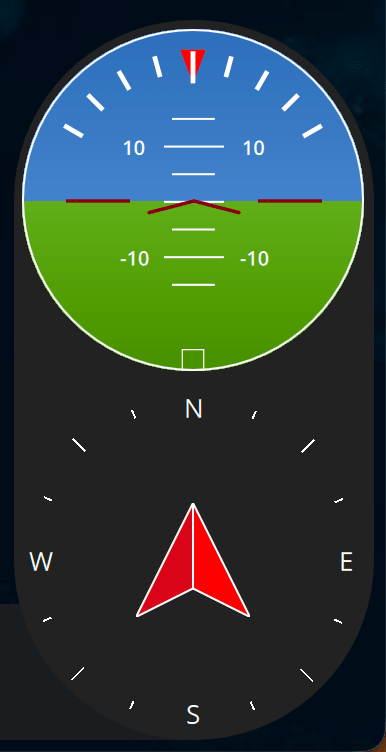
Check the attitude estimation: connect to the drone using QGroundControl, rotate the drone in different orientations and check if the attitude estimation shown in QGroundControl is correct. Attitude indicator in QGroundControl is shown below:
-
Perform motor tests in the console. Use the following commands — remove the propellers before running the tests!
mfr— should rotate front right motor (counter-clockwise).mfl— should rotate front left motor (clockwise).mrl— should rotate rear left motor (counter-clockwise).mrr— should rotate rear right motor (clockwise).
Rotation diagram:
Warning
Never run the motors when powering the drone from USB, always use the battery for that.
Setup remote control
There are several ways to control the drone's flight: using smartphone (Wi-Fi), using SBUS remote control, or using USB remote control (Wi-Fi).
Control with smartphone
- Install QGroundControl mobile app on your smartphone.
- Power the drone using the battery.
- Connect your smartphone to the appeared
flixWi-Fi network (password:flixwifi). - Open QGroundControl app. It should connect and begin showing the drone's telemetry automatically.
- Go to the settings and enable Virtual Joystick. Auto-Center Throttle setting should be disabled.
- Use the virtual joystick to fly the drone!
Tip
Decrease
CTL_TILT_MAXparameter when flying using the smartphone to make the controls less sensitive.
Control with remote control
Before using remote SBUS-connected remote control, you need to calibrate it:
- Access the console using QGroundControl (recommended) or Serial Monitor.
- Type
crcommand and follow the instructions. - Use the remote control to fly the drone!
Control with USB remote control
If your drone doesn't have RC receiver installed, you can use USB remote control and QGroundControl app to fly it.
- Install QGroundControl app on your computer.
- Connect your USB remote control to the computer.
- Power up the drone.
- Connect your computer to the appeared
flixWi-Fi network (password:flixwifi). - Launch QGroundControl app. It should connect and begin showing the drone's telemetry automatically.
- Go the the QGroundControl menu ⇒ Vehicle Setup ⇒ Joystick. Calibrate you USB remote control there.
- Use the USB remote control to fly the drone!
Flight
For both virtual sticks and a physical joystick, the default control scheme is left stick for throttle and yaw and right stick for pitch and roll:

Arming and disarming
To start the motors, you should arm the drone. To do that, move the left stick to the bottom right corner:

After that, the motors will start spinning at low speed, indicating that the drone is armed and ready to fly.
When finished flying, disarm the drone, moving the left stick to the bottom left corner:

Note
If something goes wrong, go to the Troubleshooting article.
Flight modes
Flight mode is changed using mode switch on the remote control or using the command line.
STAB
The default mode is STAB. In this mode, the drone stabilizes its attitude (orientation). The left stick controls throttle and yaw rate, the right stick controls pitch and roll angles.
Important
The drone doesn't stabilize its position, so slight drift is possible. The pilot should compensate it manually.
ACRO
In this mode, the pilot controls the angular rates. This control method is difficult to fly and mostly used in FPV racing.
RAW
RAW mode disables all the stabilization, and the pilot inputs are mixed directly to the motors. The IMU sensor is not involved. This mode is intended for testing and demonstration purposes only, and basically the drone cannot fly in this mode.
AUTO
In this mode, the pilot inputs are ignored (except the mode switch, if configured). The drone can be controlled using pyflix Python library, or by modifying the firmware to implement the needed autonomous behavior.
If the pilot moves the control sticks, the drone will switch back to STAB mode.
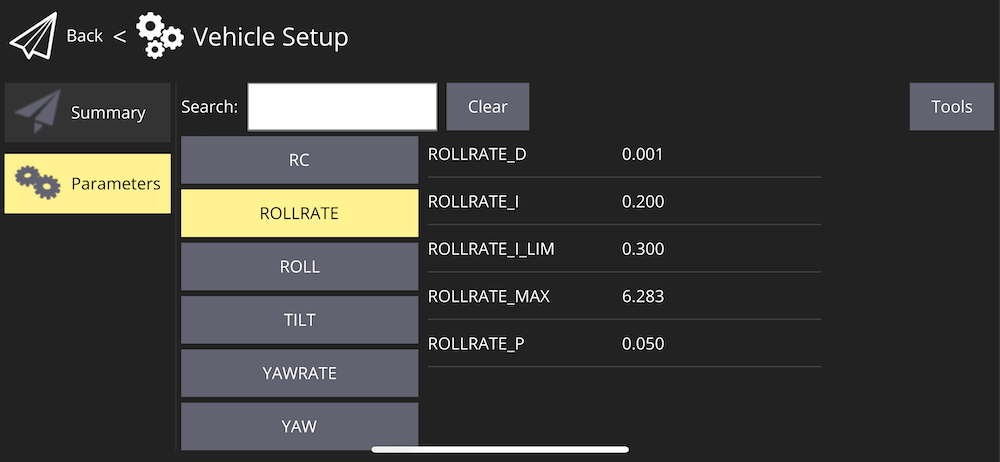
Adjusting parameters
You can adjust some of the drone's parameters (include PID coefficients) in QGroundControl. In order to do that, go to the QGroundControl menu ⇒ Vehicle Setup ⇒ Parameters.
Flight log
After the flight, you can download the flight log for analysis wirelessly. Use the following for that:
make log
See more details about log analysis in the log analysis article.
