8.8 KiB
Flix Python library
The Flix Python library allows you to remotely connect to a Flix quadcopter. It provides access to telemetry data, supports executing console commands, and controlling the drone's flight.
To use the library, connect to the drone's Wi-Fi. To use it with the simulator, ensure the script runs on the same network as the simulator.
Installation
If you have cloned the repo, install the library from the repo:
cd /path/to/flix/repo
pip install -e tools
Alternatively, install from pip:
pip install pyflix
Usage
The API is accessed through the Flix class:
from flix import Flix
flix = Flix() # create a Flix object and wait for connection
Telemetry
Basic telemetry is available through object properties. The property names generally match the corresponding variables in the firmware itself:
print(flix.connected) # True if connected to the drone
print(flix.mode) # current flight mode (str)
print(flix.armed) # True if the drone is armed
print(flix.landed) # True if the drone is landed
print(flix.attitude) # attitude quaternion [w, x, y, z]
print(flix.attitude_euler) # attitude as Euler angles [roll, pitch, yaw]
print(flix.rates) # angular rates [roll_rate, pitch_rate, yaw_rate]
print(flix.channels) # raw RC channels (list)
print(flix.motors) # motor outputs (list)
print(flix.acc) # accelerometer output (list)
print(flix.gyro) # gyroscope output (list)
The library uses the Front-Left-Up coordinate system — the same as the firmware:

All angles are in radians.
Events
The Flix object implements the Observable pattern, allowing to listen for events. You can subscribe to events using on method:
flix.on('connected', lambda: print('Connected to Flix'))
flix.on('disconnected', lambda: print('Disconnected from Flix'))
flix.on('print', lambda text: print(f'Flix says: {text}'))
Unsubscribe from events using off method:
flix.off('print') # unsubscribe from print events
flix.off(callback) # unsubscribe specific callback
You can also wait for specific events using wait method. This method returns the data associated with the event:
gyro = flix.wait('gyro') # wait for gyroscope update
attitude = flix.wait('attitude', timeout=3) # wait for attitude update, raise TimeoutError after 3 seconds
The second argument (value) specifies a condition for filtering events. It can be either an expected value or a callable:
flix.wait('armed', True) # wait until armed
flix.wait('armed', False) # wait until disarmed
flix.wait('mode', 'AUTO') # wait until flight mode is switched to AUTO
flix.wait('motors', lambda motors: not any(motors)) # wait until all motors stop
flix.wait('attitude_euler', lambda att: att[0] > 0) # wait until roll angle is positive
Full list of events:
| Event | Description | Associated data |
|---|---|---|
connected |
Connected to the drone | |
disconnected |
Connection is lost | |
armed |
Armed state update | Armed state (bool) |
mode |
Flight mode update | Flight mode (str) |
landed |
Landed state update | Landed state (bool) |
print |
The drone prints text to the console | Text |
attitude |
Attitude update | Attitude quaternion (list) |
attitude_euler |
Attitude update | Euler angles (list) |
rates |
Angular rates update | Angular rates (list) |
channels |
Raw RC channels update | Raw RC channels (list) |
motors |
Motor outputs update | Motor outputs (list) |
acc |
Accelerometer update | Accelerometer output (list) |
gyro |
Gyroscope update | Gyroscope output (list) |
mavlink |
Received MAVLink message | Message object |
mavlink.<message_name> |
Received specific MAVLink message | Message object |
mavlink.<message_id> |
Received specific MAVLink message | Message object |
value |
Named value update (see below) | Name, value |
value.<name> |
Specific named value update (see below) | Value |
Note
Update events trigger on every new piece of data from the drone, and do not mean the value has changed.
Basic methods
Get and set firmware parameters using get_param and set_param methods:
pitch_p = flix.get_param('PITCH_P') # get parameter value
flix.set_param('PITCH_P', 5) # set parameter value
Execute console commands using cli method. This method returns the command response:
imu = flix.cli('imu') # get detailed IMU data
time = flix.cli('time') # get detailed time data
flix.cli('reboot') # reboot the drone
Tip
Use
helpcommand to get the list of available commands.
You can arm and disarm the drone using set_armed method (warning: the drone will fall if disarmed in the air):
flix.set_armed(True) # arm the drone
flix.set_armed(False) # disarm the drone
You can pass pilot's controls using set_controls method:
flix.set_controls(roll=0, pitch=0, yaw=0, throttle=0.6)
Warning
This method is not intended for automatic flights, only for adding support for a custom pilot input device.
Automatic flight
To perform automatic flight, switch the mode to AUTO, either from the remote control, or from the code:
flix.set_mode('AUTO')
In this mode you can set flight control targets. Setting attitude target:
flix.set_attitude([0.1, 0.2, 0.3], 0.6) # set target roll, pitch, yaw and thrust
flix.set_attitude([1, 0, 0, 0], 0.6) # set target attitude quaternion and thrust
Setting angular rates target:
flix.set_rates([0.1, 0.2, 0.3], 0.6) # set target roll rate, pitch rate, yaw rate and thrust
You also can control raw motor outputs directly:
flix.set_motors([0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5]) # set motor outputs in range [0, 1]
In AUTO mode, the drone will arm automatically if the thrust is greater than zero, and disarm if thrust is zero. Therefore, to disarm the drone, set thrust to zero:
flix.set_attitude([0, 0, 0], 0) # disarm the drone
The following methods are in development and are not functional yet:
set_position— set target position.set_velocity— set target velocity.
To exit AUTO mode move control sticks and the drone will switch to STAB mode.
Usage alongside QGroundControl
You can use the Flix library alongside the QGroundControl app, using proxy mode. To do that:
-
Run proxy for
pyflixand QGroundControl in background:flix-proxy -
Go to QGroundControl settings ⇒ Comm Links.
-
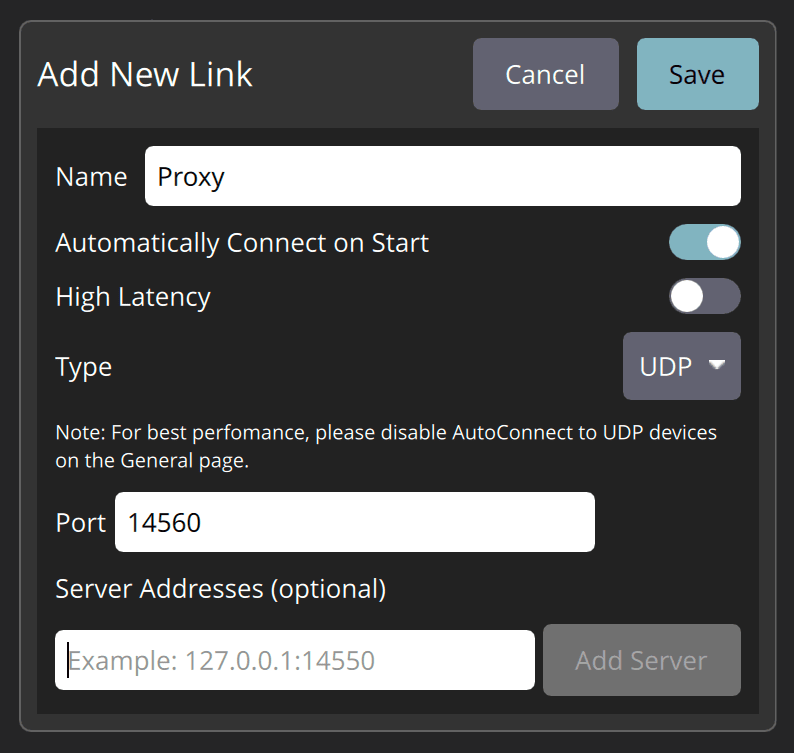
Add new link with the following settings:
- Name: Proxy
- Automatically Connect on Start: ✓
- Type: UDP
- Port: 14560
-
Restart QGroundControl.
Now you can run pyflix scripts and QGroundControl simultaneously.
Tools
The following scripts demonstrate how to use the library:
cli.py— remote access to the drone's command line interface.log.py— download flight logs from the drone.example.py— a simple example, prints telemetry data and waits for events.
Advanced usage
MAVLink
You can access the most recently received messages using messages property:
print(flix.messages.get('HEARTBEAT')) # print the latest HEARTBEAT message
You can wait for a specific message using wait method:
heartbeat = flix.wait('mavlink.HEARTBEAT')
You can send raw messages using mavlink property:
from pymavlink.dialects.v20 import common as mavlink
flix.mavlink.heartbeat_send(mavlink.MAV_TYPE_GCS, mavlink.MAV_AUTOPILOT_INVALID,
mavlink.MAV_MODE_FLAG_CUSTOM_MODE_ENABLED, 0, 0)
Named values
You can pass arbitrary named values from the firmware to the Python script using NAMED_VALUE_FLOAT, NAMED_VALUE_INT, DEBUG, DEBUG_VECT, and DEBUG_FLOAT_ARRAY MAVLink messages.
All these named values will appear in the values dictionary:
print(flix.values['some_value'])
print(flix.values['some_vector'])
You can send values from the firmware like this (mavlink.ino):
// Send float named value
mavlink_msg_named_value_float_pack(SYSTEM_ID, MAV_COMP_ID_AUTOPILOT1, &msg, t, "loop_rate", loopRate);
sendMessage(&msg);
// Send vector named value
mavlink_msg_debug_vect_pack(SYSTEM_ID, MAV_COMP_ID_AUTOPILOT1, &msg, "gyro_bias", t, gyroBias.x, gyroBias.y, gyroBias.z);
sendMessage(&msg);
Logging
You can control Flix library verbosity using Python's logging module:
import logging
logger = logging.getLogger('flix')
logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG) # be more verbose
logger.setLevel(logging.WARNING) # be less verbose
Stability
The library is in development stage. The API is not stable.